|
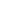
Battle of Little Bighorn |
Also known as Custer's Last Stand or the Battle of the Greasy Grass, it was an armed engagement between combined forces of Lakota, Northern Cheyenne and Arapaho people against the 7th Cavalry Regiment of the United States Army on June 25 and 26, 1876 near the Little Bighorn River in eastern Montana Territory. It was an overwhelming victory for the Lakota, Northern Cheyenne, and Arapaho, led by several major war leaders, including Crazy Horse and Gall, inspired by the visions of Sitting Bull (Tȟatȟáŋka Íyotake). The U.S. Seventh Cavalry and a battalion of 700 men led by George Armstrong Custer, suffered severe defeat. |
|
|
Battle of Wood Lake |
The last battle of the U.S.-Dakota War in September, 1862, between Dakota and U.S. military forces.
|
|
|
Battle of Wounded Knee |
The last major battle perpetrated by the U.S. government against the Dakota, Lakota, and Nakota Oyate (Sioux) on December 29, 1890. |
|
|
BIA |
Bureau of Indian Affairs |
|
|
Big Eagle (Wambditanka) |
Wambditanka (Great War Eagle). A chief of one of the bands of Mdewakanton Dakota at the time of the U.S.-Dakota War in 1862; commonly called Big Eagle, and sometimes known as Jerome Big Eagle. |
|
|
Birch Coulee |
A battle location of the U.S.-Dakota War of 1862 located near Morton, Minnesota. |
|
|
Bishop Henry Whipple |
The first Episcopal bishop of Minnesota who was a missionary to the Dakota people. |
|
|
Boarding School (Native American/Indian) |
A school managed and regulated by the government to assimilate Native Americans into White society. Called "residential schools" in Canada. |
|
|
Bounty |
An amount of money or other reward offered by an organization for the capture of a person or thing. In this case, refers to U.S. government money (up to $200 in the late 1860s) rewarded to people for the capture of Dakota (often also Lakota and/or Nakota) people during the Punitive Expeditions after the U.S.-Dakota War. |
|
|
Bureau of Indian Affairs |
Created in 1824, it is responsible for delivering a broad range of services to Federally-recognized Indian tribes and their members. |
|
|
Burlington Northern |
A railroad company formed by the merger of the Great Northern, the Northern Pacific, the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy, Spokane, Portland and Seattle railroad companies. |
|